Compared to machine-made rugs, hand-knotted rugs usually have a lower carbon footprint because they use natural fibers, require less energy, and are often crafted locally. Machine-made rugs rely on energy-intensive machinery, synthetic fibers, and mass production, which increase emissions and waste. Choosing a handmade rug supports sustainability, durability, and eco-friendly materials. To understand how these factors impact their environmental effects and help you make a smarter choice, explore the details further.
Key Takeaways
- Hand-knotted rugs generally have a lower carbon footprint due to manual labor and natural materials, reducing energy consumption.
- Machine-made rugs consume more energy through automation, synthetic fiber production, and chemical dyeing processes.
- Natural fibers in hand-knotted rugs are biodegradable, whereas synthetic fibers in machine-made rugs contribute to persistent plastic waste.
- Locally sourced, hand-crafted rugs typically result in lower transportation emissions compared to imported machine-made rugs.
- Durability of hand-knotted rugs decreases replacement frequency, further reducing overall carbon emissions over their lifespan.
Overview of Rug Manufacturing Methods

Rug manufacturing primarily occurs through two methods: machine-made and hand-knotted. Machine-made rugs are produced using automated processes, often involving synthetic fibers like polypropylene or nylon, which are durable and cost-effective. These rugs typically utilize advanced dyeing techniques, such as digital printing or mass dyeing, to achieve vibrant, uniform colors quickly. In contrast, hand-knotted rugs are crafted manually, often with natural fibers like wool or silk, and involve intricate knotting techniques that require skill and time. While synthetic fibers dominate machine-made rugs for their affordability, natural fibers are favored in hand-knotted rugs for their authenticity. Both methods influence the rug’s overall quality, appearance, and environmental footprint, which are important factors to contemplate when evaluating their sustainability. Additionally, the production process of each method significantly impacts their ecological impact, with machine-made rugs generally having a larger carbon footprint due to automation and synthetic materials. Moreover, the material selection plays a crucial role in the environmental implications of each approach.
Environmental Impact of Machine-Made Rugs

Machine-made rugs typically have a significant environmental impact due to their production processes and material choices. Many rely on chemical dyes that can release harmful pollutants into the environment, contributing to water and air pollution. Additionally, these rugs often feature plastic backing, which is derived from non-renewable petroleum sources and adds to plastic waste when discarded. The production process consumes substantial energy, especially in mass manufacturing facilities, increasing carbon emissions. The use of synthetic materials and chemical dyes not only affects ecosystems but also poses health risks for workers and consumers. Moreover, the energy consumption associated with large-scale manufacturing contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. Overall, the environmental footprint of machine-made rugs is heightened by their reliance on non-biodegradable components and energy-intensive manufacturing, making them less eco-friendly compared to natural, hand-made alternatives. Risks associated with production also include security vulnerabilities and regulatory compliance challenges that can further impact environmental sustainability efforts.
Production Process of Hand-Knotted Rugs
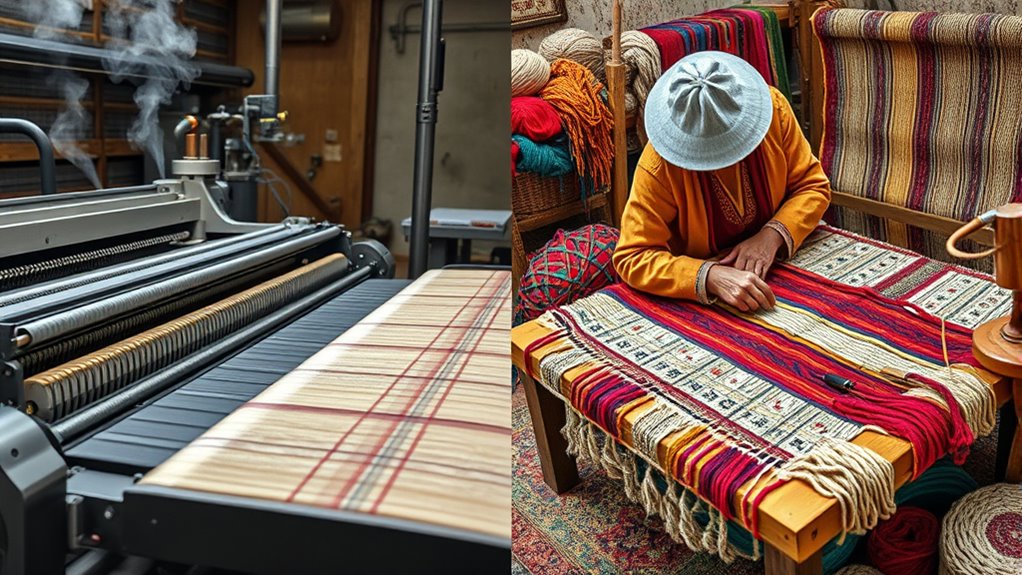

The production process of hand-knotted rugs involves a meticulous and labor-intensive craft that has been passed down through generations. You start with selecting wool, silk, or cotton fibers, which are then dyed using traditional dyeing techniques. These methods often involve natural dyes, contributing to the rug’s unique color variations. Each knot is carefully tied by hand onto a foundation, creating intricate patterns and design variability that reflect regional styles and artisans’ creativity. Unlike machine-made rugs, this process requires patience and skill, ensuring high-quality craftsmanship. The dyeing techniques influence the rug’s appearance and sustainability, as natural dyes tend to have a lower environmental impact. Natural dyeing techniques are a key aspect that enhances both the beauty and eco-friendliness of hand-knotted rugs. Additionally, the value of these rugs is often linked to the complexity and artistry of the weaving process, making each piece a unique work of art. Overall, the handcrafted process emphasizes artistry and sustainability, making each rug a one-of-a-kind piece.
Energy Consumption in Machine-Made Rug Production

You’ll find that producing machine-made rugs requires significant energy, mainly due to manufacturing demands. Automation speeds up the process but also increases power consumption. Understanding how these factors influence the overall carbon footprint helps you compare machine-made and hand-knotted rugs more effectively. Additionally, selecting reliable production practices can reduce environmental impact. Moreover, advancements in energy-efficient machinery can further decrease the carbon footprint associated with mass production. Considering the types of materials used can also impact energy consumption, as some materials require more intensive processing. Incorporating sustainable manufacturing methods can further mitigate environmental effects and promote eco-friendly practices.
Manufacturing Energy Demands
Producing machine-made rugs requires significant energy input, as automated manufacturing processes rely heavily on electricity and mechanical power. This energy is used to operate machinery that manipulates synthetic fibers, which often undergo chemical treatments to enhance durability and appearance. The manufacturing process consumes energy at multiple stages, from fiber production to final finishing. Vetted – Startup Sofa Additionally, the use of synthetic fibers involves energy-intensive processes such as polymerization and extrusion, further increasing overall energy consumption. Synthetic fiber production demands significant energy input, often relying on fossil fuels, which contributes to higher emissions.
- Powering large weaving machines
- Heating and curing chemical treatments
- Producing synthetic fibers
- Operating dyeing equipment
- Maintaining production lines
Automation and Power Use
Automation considerably drives the energy consumption in machine-made rug production, as advanced machinery requires continuous power to operate. Robotic automation streamlines manufacturing processes, increasing productivity but also increasing electricity use. While these machines are designed to be energy-efficient, their constant operation means higher overall energy consumption compared to traditional hand-knotting. Modern factories often incorporate energy-efficient technologies to reduce their carbon footprint, but the reliance on power remains significant. The balance between automation’s productivity benefits and its energy demands is vital in evaluating the environmental impact of machine-made rugs. Additionally, the integration of AI security measures can help monitor and optimize energy consumption in manufacturing facilities. To sum up, automation boosts efficiency but also raises energy use, making it a key factor in understanding the overall carbon footprint of machine-made rug production.
Manual Labor and Sustainability in Hand-Knotted Rugs
Hand-knotted rugs require significant manual labor, which can lead to higher emissions but also supports local economies. Sourcing materials locally reduces transportation impact and promotes sustainability. The craftsmanship often results in durable rugs that last longer, making them a more sustainable choice over time. Additionally, emotional alignment during the creation process can enhance the vibrational energy embedded in the rug, contributing to its overall positive influence in the home. Implementing cost-effective strategies for asset division in the sourcing and production process can further enhance sustainability efforts by optimizing resource use and minimizing waste. Cultivating a growth mindset among artisans can lead to continuous improvement in techniques and sustainability practices. Incorporating human-centered methodologies can help artisans adapt innovative practices that balance tradition with environmental consciousness.
Labor Intensity and Emissions
Although hand-knotted rugs require significant manual effort, this labor-intensive process often results in lower emissions compared to machine-made counterparts. By using artisanal techniques, artisans work carefully, reducing energy consumption typically associated with industrial processes. This approach also promotes cultural preservation, keeping traditional skills alive and reducing reliance on mass production. Additionally, in regions where traditional craftsmanship is valued, hand-knotting supports cultural heritage and local economies. You’ll find that:
- Manual craftsmanship minimizes energy use
- Artisanal techniques encourage sustainable practices
- Cultural preservation supports local communities
- Hand-knotting avoids large-scale machinery emissions
- The process emphasizes quality over quantity, fostering sustainable craftsmanship.
Furthermore, the use of natural and locally sourced materials in hand-knotting can further reduce environmental impact. While labor is intensive, the overall carbon footprint is often lower, making hand-knotted rugs a more sustainable choice. This method highlights the importance of human effort in creating environmentally conscious products that celebrate cultural heritage. Additionally, embracing traditional methods can inspire innovative approaches to sustainable manufacturing.
Local Material Sourcing
By sourcing materials locally, you help artisans reduce the environmental impact associated with transportation and long supply chains. Local sourcing allows artisans to select eco friendly materials that are often more sustainable and have a smaller carbon footprint. Using locally available resources minimizes the need for extensive shipping, lowering greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. It also encourages the use of natural fibers like wool, hemp, or cotton, which are biodegradable and require fewer chemicals compared to synthetic alternatives. Additionally, local sourcing supports regional ecosystems and economies, fostering more sustainable practices. By choosing hand-knotted rugs made with locally sourced, eco friendly materials, you promote a more environmentally conscious approach that respects natural resources and reduces overall carbon emissions. Incorporating AI data analysis can further optimize material selection and supply chain efficiency, enhancing sustainability efforts.
Craftsmanship and Longevity
Craftsmanship and longevity are at the heart of sustainable rug production, as the skill and care invested in each piece guarantee it lasts for decades rather than years. When you choose hand-knotted rugs, you benefit from artisanal craftsmanship that emphasizes meticulous detail and quality. These rugs are built to stand the test of time, thanks to material longevity and durable construction. The craftsmanship ensures each knot is tightly woven, reducing the need for replacements. Additionally, these rugs often use natural, sustainable materials that age gracefully. Investing in a hand-knotted rug means you’re supporting traditional techniques and creating a long-lasting product.
- Skilled artisans dedicate hours to each rug
- Natural fibers improve durability
- Timeless designs prevent quick obsolescence
- Proper care extends lifespan
- Reduced need for frequent replacement
Material Use and Waste Management

Material use and waste management differ substantially between machine-made and hand-knotted rugs. Machine-made rugs often rely on synthetic fibers, which are derived from petrochemicals and can involve extensive chemical treatments during manufacturing. These synthetic materials are less biodegradable, leading to increased waste when the rugs are discarded. Additionally, mass production generates more offcuts and defective products, which often end up as landfill waste. In contrast, hand-knotted rugs typically use natural fibers like wool, silk, or cotton, which are renewable and biodegradable. Waste is minimized because artisans often reuse leftover materials, and fewer chemical treatments are involved. This eco-friendlier approach reduces environmental impact and helps manage waste more sustainably over the rug’s lifecycle.
Lifespan and Durability Considerations

When evaluating the environmental impact of rugs, lifespan and durability play crucial roles. Rugs that last longer reduce the need for frequent replacements, lowering overall carbon footprints. Hand-knotted rugs often meet high sustainability standards due to their craftsmanship and repairability options, enabling you to extend their life. Machine-made rugs may have shorter lifespans but can be more uniform and easier to replace if needed. Consider these factors:
- Quality materials that resist wear and tear
- Ease of repair and availability of repair services
- Construction techniques aligned with sustainability standards
- Resistance to fading and damage
- The ability to refurbish or reupholster parts
Recycling and End-of-Life Disposal

Recycling and end-of-life disposal are critical factors in evaluating a rug’s environmental impact. Your choice of recycling practices can markedly reduce waste, especially when rugs are made from natural or recyclable materials. Hand-knotted rugs often use wool, silk, or cotton, which can sometimes be repurposed or recycled more easily than synthetic fibers. Disposal methods matter too; landfilling synthetic rugs releases toxins, while burning releases greenhouse gases. Proper disposal methods, like donating or recycling, help extend a rug’s life cycle and minimize environmental harm. Machine-made rugs, often containing synthetic fibers, pose challenges for recycling, but some manufacturers now develop programs for eco-friendly disposal. By understanding these options, you can make more environmentally responsible decisions at the end of a rug’s life.
Making an Eco-Conscious Choice: Factors to Consider

Choosing an eco-conscious rug involves evaluating several key factors that impact its overall environmental footprint. First, consider whether the rug uses eco friendly dyes, which reduce chemical waste and pollution. Next, look into the manufacturer’s efforts in carbon offsetting, helping balance out emissions from production and transportation. Also, assess the materials—natural fibers like wool or jute are more sustainable than synthetic options. Durability and lifespan matter too; a longer-lasting rug minimizes waste. Finally, research whether the rug is made locally to cut down transportation emissions and support local economies. These factors guide you toward a greener choice, ensuring your rug aligns with eco-friendly principles and reduces your carbon footprint.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Transportation Methods Affect the Overall Carbon Footprint of Rugs?
Transportation methods considerably impact the overall carbon footprint of rugs through transportation emissions. When you choose faster shipping options or air freight, shipping logistics increase emissions, raising the rug’s carbon footprint. Conversely, opting for sea freight or land transportation reduces emissions, making your choice more eco-friendly. Your decisions about transportation methods directly influence the environmental impact, emphasizing the importance of considering shipping logistics to minimize your rug’s carbon footprint.
What Certifications Indicate Environmentally Friendly Rug Manufacturing?
Think of eco labels as green flags waving proudly. When you look for sustainable certifications like OEKO-TEX, Green Label Plus, or GOTS, you guarantee your rug’s made with eco-friendly practices. These standards, falling under eco label standards, assure low environmental impact, safer materials, and responsible manufacturing. By choosing rugs with these certifications, you support sustainability and reduce your ecological footprint, turning your home into a greener haven.
Are There Differences in Chemical Emissions Between Machine-Made and Hand-Knotted Rugs?
You might wonder if chemical emissions differ between machine-made and hand-knotted rugs. Generally, machine-made rugs often use synthetic chemicals in dyes and backing materials, leading to higher emission levels. Hand-knotted rugs typically involve fewer synthetic chemicals, resulting in lower emissions. By choosing hand-knotted options, you can reduce exposure to potentially harmful chemicals and minimize environmental impact, making them a more eco-friendly choice overall.
How Do Dyeing Processes Impact a Rug’S Environmental Footprint?
Dyeing processes are like the heartbeats of a rug’s environmental story. When you choose natural dyes, you’re opting for a gentler, eco-friendly rhythm that reduces harmful chemicals and water pollution. Synthetic dyes, while vibrant, often leave a darker stain on our planet’s health due to their chemical-heavy production. By understanding this, you can make more sustainable choices, turning your rug into a symbol of beauty and environmental care.
Can Choosing Locally Made Rugs Reduce Overall Environmental Impact?
Choosing locally made rugs can considerably reduce your environmental impact. By prioritizing local sourcing, you support regional eco initiatives that promote sustainable practices and reduce transportation emissions. When you buy from nearby artisans, you help lower the overall carbon footprint associated with long-distance shipping. Plus, supporting regional efforts encourages eco-friendly production methods, making your choice both stylish and environmentally responsible.
Conclusion
Choosing between machine-made and hand-knotted rugs isn’t just a matter of style—it’s about making a difference. By understanding their environmental impacts, you hold the power to turn your home into a sanctuary for the planet. Hand-knotted rugs, with their timeless craftsmanship, can dramatically reduce your carbon footprint and save resources. Make an eco-conscious choice today; your decision could be the ripple that sparks a tidal wave of change for future generations.









