Microfading tests measure how sensitive artifacts are to light exposure, helping you understand when damage might occur. Using focused light sources and precise sensors, you can assess the fading rate and identify vulnerable areas. This non-invasive approach provides valuable data to inform your preservation strategies and prevent irreversible harm. If you continue exploring, you’ll discover how this technique enhances material assessment and supports better conservation decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Microfading tests measure color and brightness changes in small areas to quantify an artifact’s light sensitivity accurately.
- Controlled light exposure during testing helps identify thresholds where fading begins, informing preservation limits.
- Calibration of sensors and photographic references ensures precise quantification of fading rates over time.
- Data trends from microfading reveal material vulnerability, guiding conservation decisions to prevent irreversible damage.
- Non-destructive and localized, microfading provides reliable light sensitivity assessment without harming valuable cultural heritage objects.
Understanding Light Sensitivity in Cultural Heritage

Understanding light sensitivity in cultural heritage is essential because many artifacts and artworks are highly vulnerable to damage caused by exposure to light. Light adaptation plays a key role in how materials respond to illumination, influencing pigment deterioration over time. When artworks are exposed to light, their pigments undergo chemical changes, leading to fading or discoloration. Recognizing this sensitivity helps conservators develop strategies to limit light exposure, preserving the integrity of the pieces. By understanding how light impacts materials at a microscopic level, you can better assess the potential risks involved in display and storage. This knowledge underscores the importance of controlling light levels and duration, ultimately safeguarding cultural heritage from irreversible damage caused by prolonged or intense illumination. Additionally, advances in microfading tests allow for precise measurement of light sensitivity, enabling more effective preservation strategies.
The Fundamentals of Microfading Testing

Microfading testing offers a precise way to evaluate how specific areas of an artifact respond to light exposure. It relies on careful sensor calibration to guarantee measurements accurately reflect the artifact’s fading behavior. This process involves calibrating the sensor to account for its sensitivity and linearity, which is essential for reliable results. Photographic calibration is also vital, as it helps translate sensor data into meaningful color and brightness changes. Understanding these calibration steps ensures your microfading tests are both accurate and reproducible. By establishing a controlled testing environment, you can detect subtle changes in light sensitivity that might otherwise go unnoticed. Mastering these fundamentals enables you to assess an artifact’s vulnerability to light, guiding preservation strategies effectively. Additionally, incorporating AI-powered analysis can enhance the interpretation of data, leading to more informed conservation decisions.
Equipment and Techniques Used in Microfading Analysis
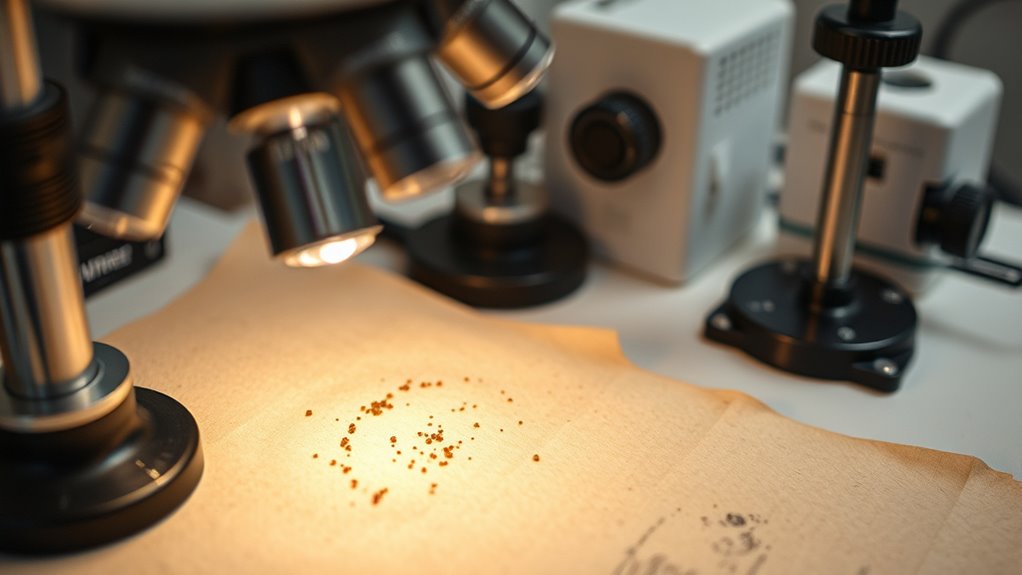
To accurately assess how artifacts respond to light exposure, you need specialized equipment designed for microfading analysis. First, guarantee your spectrometer is properly calibrated; this guarantees precise measurements of light reflectance and fluorescence. The calibration process involves using certified standards to adjust the instrument’s response, maintaining accuracy over time. Next, sample preparation is vital: you must carefully select and position the artifact to avoid damage and ensure consistent illumination. A focused light source, such as a fiber optic or LED, directs controlled light onto the sample. You may also use a microprobe to target specific areas, minimizing variability. Combining meticulous sample preparation with accurate spectrometer calibration helps you obtain reliable data, allowing you to quantify light sensitivity with confidence. Additionally, employing appropriate lighting conditions ensures the integrity of the measurements and the safety of sensitive materials.
Interpreting Microfading Data for Conservation Decisions

Analyzing microfading data helps you identify which materials are most at risk of fading and deterioration. By recognizing data trends, you can make informed decisions about prioritizing conservation efforts. This approach guarantees your strategies are targeted and effective in preserving fragile artworks. Additionally, understanding the beneficial ingredients in treatments can inform maintenance routines and enhance long-term preservation.
Data Trends Analysis
Interpreting microfading data effectively requires understanding the trends and patterns that emerge over time. By analyzing these trends, you can identify how light exposure affects color matching and material degradation. Look for steady increases in fading rates, which indicate heightened sensitivity and potential risks to the artifact’s appearance and stability. Sudden changes or plateaus may suggest temporary stabilization or the need for closer inspection. Comparing data points across different areas helps pinpoint vulnerable regions needing prioritized conservation. Recognizing consistent patterns enables you to predict future deterioration, guiding decisions on light exposure limits. Incorporating preventive conservation strategies can further safeguard the artifact’s condition. This detailed trend analysis ensures you’re making informed choices to preserve the artifact’s integrity while balancing necessary display or storage conditions.
Conservation Strategy Insights
Understanding microfading data is vital for making informed conservation decisions. By analyzing how different materials respond to light, you can tailor strategies that minimize damage. Recognize the historical context to understand past exposures and deterioration patterns, which helps predict future risks. Material variability plays a significant role; some substances are more sensitive than others, requiring specific handling or display conditions. Microfading tests reveal which areas or materials are most vulnerable, guiding you to prioritize treatment or protective measures. This targeted approach ensures resources are used effectively, reducing unnecessary interventions. Additionally, the incorporation of antioxidants in conservation treatments can help mitigate light-induced deterioration of sensitive materials. Ultimately, interpreting microfading data empowers you to develop conservation plans that respect the original material qualities while safeguarding the artifact’s longevity.
Advantages of Microfading Over Traditional Light Testing Methods

Microfading offers a more precise way to assess damage without risking further harm to delicate materials. It allows you to measure color changes accurately in a tiny area, unlike traditional methods that often require larger samples. This non-destructive approach helps you make informed conservation decisions while preserving the integrity of the artifact. Incorporating low carb foods into your diet can also promote overall health and energy, supporting the well-being of those working in preservation and conservation fields.
Precise Damage Assessment
Microfading offers a level of precision in damage assessment that traditional light testing methods can’t match. With microfading, you can detect subtle artifact degradation caused by display lighting, which often goes unnoticed with conventional techniques. This method allows you to measure how specific areas respond to very low light levels, providing detailed insights into the material’s sensitivity. Unlike broader tests, microfading pinpoints damage thresholds accurately, helping you evaluate potential risks before visible deterioration occurs. This targeted approach minimizes unnecessary exposure, protecting valuable artifacts from further harm. By accurately quantifying light sensitivity, you gain better control over preservation strategies, ensuring that display lighting remains safe while maintaining ideal viewing conditions. Additionally, integrating AI-powered data analytics can enhance the interpretation of microfading results, leading to more informed conservation decisions. Ultimately, microfading enhances your ability to assess damage risk with greater clarity and confidence.
Non-Destructive Testing
Compared to traditional light testing methods, microfading offers a truly non-destructive way to assess artifact sensitivity without causing harm. This technique allows you to perform photographic analysis of delicate materials, revealing how they respond to light exposure without risking further damage. Unlike older methods that may accelerate material degradation or require sampling, microfading minimizes risk by measuring light sensitivity in real-time. You can evaluate a piece’s vulnerability without altering its appearance or structure, making it ideal for priceless artifacts. As a result, you gain accurate insights into how light affects the object, guiding conservation efforts while preserving the artifact’s integrity. This non-invasive approach ensures your assessments are both safe and scientifically reliable, protecting cultural heritage for future generations. Additionally, understanding the light sensitivity of artifacts helps conservators develop more effective preservation strategies.
Case Studies Demonstrating Microfading Applications

The practical applications of microfading tests become evident through various case studies that showcase their ability to assess pigment stability and identify areas vulnerable to fading. These examples reveal how microfading can detect early signs of color fading and material degradation before visible damage occurs.
Consider these key applications:
- Evaluating the lightfastness of historic pigments in paintings.
- Pinpointing fragile areas in textiles prone to fading.
- Monitoring paper and ink stability in archival materials.
In each case, microfading helps conservators predict how objects will respond to light exposure, guiding preservation strategies. By identifying vulnerable spots, you can prevent irreversible damage caused by color fading and material degradation, ensuring the longevity of priceless artifacts.
Limitations and Challenges of Microfading Testing

Despite its valuable insights, microfading testing faces several limitations that can affect its effectiveness. Sample bias can skew results if the tested area isn’t representative of the entire artifact, leading to inaccurate predictions of light sensitivity. Additionally, equipment limitations pose challenges; the precision of light sources and measurement devices can vary, impacting data consistency. Microfading tests are also sensitive to environmental conditions like humidity and temperature, which can influence results. Moreover, the small sample size might not capture the full range of material responses, and the testing process itself can cause minor damage over time. Recognizing these challenges helps you interpret microfading data more critically and emphasizes the need for standardized protocols and careful calibration. Incorporating high-quality content strategies can also improve the reliability of testing outcomes by ensuring comprehensive data collection and analysis.
Integrating Microfading Results Into Preservation Strategies

Integrating microfading results into preservation strategies requires careful interpretation of the data within the broader context of artifact conservation. You need to combine this information with digital imaging and environmental monitoring to make informed decisions. Here are key steps:
Integrate microfading data with imaging and environmental monitoring for effective preservation planning.
- Prioritize areas at highest risk based on microfading sensitivity, guiding targeted interventions.
- Use digital imaging to document baseline conditions and track deterioration over time.
- Adjust environmental controls, such as light levels and humidity, to mitigate further damage in vulnerable zones.
Future Developments in Light Sensitivity Measurement

Advancements in light sensitivity measurement are poised to revolutionize conservation practices by providing more accurate and real-time data. Future developments will focus on enhancing sensor calibration, ensuring measurements remain precise across various environments and light conditions. Improved calibration techniques will reduce errors and increase confidence in the data collected. Additionally, data visualization tools will become more sophisticated, enabling you to interpret complex light exposure patterns quickly and effectively. Interactive dashboards and real-time graphs will facilitate immediate decision-making, helping to prevent damage before it occurs. These technological improvements will make light sensitivity testing more accessible, reliable, and integrated into routine preservation workflows. As a result, you’ll better protect sensitive materials and extend the lifespan of precious artifacts through more informed, data-driven conservation strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does a Typical Microfading Test Take?
A typical microfading test usually takes around 10 to 30 minutes, depending on several factors. The test duration varies based on the sensitivity of the material, the intensity of light used, and how quickly the color change occurs. You should consider these factors influencing timing to make certain of accurate results. Keep in mind that longer tests may provide more detailed data, but they also require more careful monitoring.
Can Microfading Be Applied to Digital or Modern Materials?
You can definitely apply microfading techniques to digital materials and modern applications. This method helps assess how these contemporary items react to light exposure, ensuring they’re preserved properly. By using microfading, you can measure light sensitivity precisely, which is especially useful for digital and modern artifacts. It allows you to evaluate their longevity and develop appropriate conservation strategies, making it a valuable tool in today’s digital preservation efforts.
What Are the Safety Considerations During Microfading Testing?
Did you know that even brief light exposure can damage delicate materials? During microfading testing, you should handle samples carefully to prevent unnecessary exposure and deterioration. Always use minimal light levels and protective equipment, and guarantee proper sample handling to avoid contamination or damage. By following these safety considerations, you safeguard the integrity of your materials while accurately measuring their light sensitivity.
Is Specialized Training Required to Perform Microfading Tests?
You don’t necessarily need specialized training to perform microfading tests, but having a certain skill level definitely helps. Proper training guarantees you understand the equipment, technique, and safety considerations. It also improves your ability to interpret results accurately. While some basic knowledge might be enough for simple assessments, advanced understanding and proper skill development through training are recommended to get reliable, consistent data during microfading testing.
How Repeatable Are Microfading Measurements Over Time?
You might wonder about the measurement consistency of microfading tests over time. These measurements can be quite repeatable when you control environmental effects, such as light, temperature, and humidity, which considerably influence results. Consistent technique, calibration, and careful handling help guarantee reliable data. While some variability can occur, proper procedures and environmental stability allow you to confidently track light sensitivity changes in artworks or materials over multiple testing sessions.
Conclusion
As you explore microfading testing, you realize it’s a powerful tool for understanding light sensitivity. But the true potential lies ahead—what new insights could this technique unfasten for preserving our most fragile treasures? With ongoing advancements, microfading might soon reveal secrets that change how you protect cultural heritage forever. The question is, are you ready to embrace the future of light sensitivity measurement and uncover what’s yet to be discovered?









